What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics – with examples
What is the difference between microeconomics
and macroeconomics
In this article, as briefly as possible, what is the difference between macroeconomics and microeconomics. Some economists believe that understanding these differences is the very essence of economics.
We will not throw such loud words, but we will deal with the question.
The content of the article:
1 What macroeconomics and microeconomics study
2 Macroeconomics and microeconomics: similarities and differences
2.1 The cardinal differences between macroeconomics and microeconomics are as follows:
3 Macroeconomics and microeconomics: examples
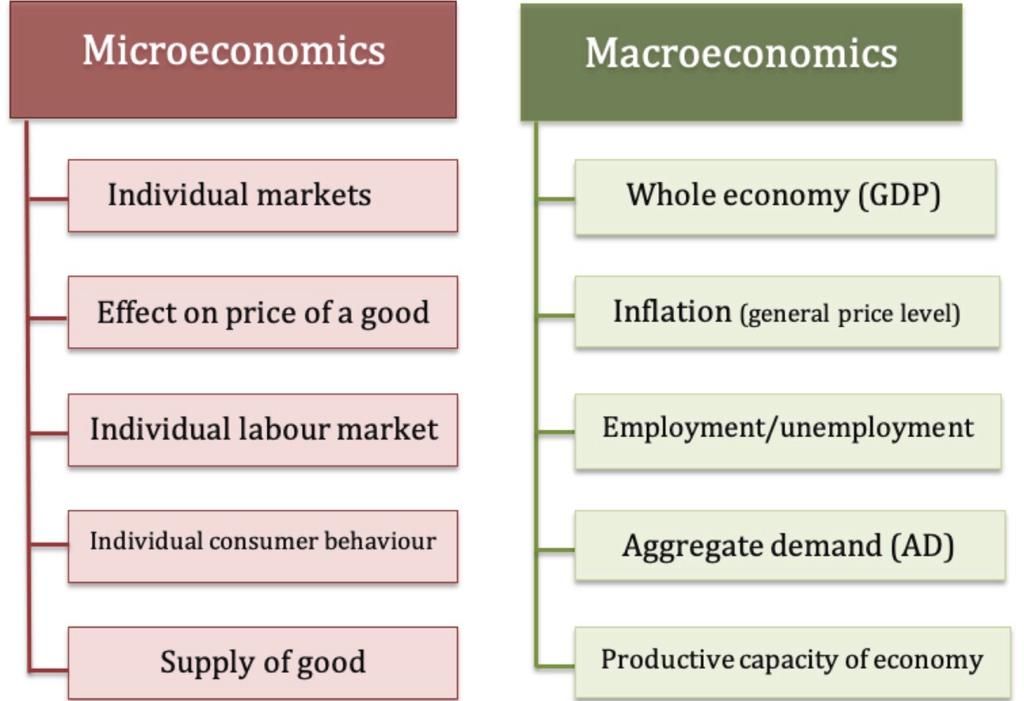
What macroeconomics and microeconomics
study The subject of study of macroeconomics is global trends:
How the authorities regulate (should regulate) economic growth
How countries interact in the world market
How to reduce unemployment
How the economy of one country affects other countries
How to avoid global economic crises? – this, unfortunately, fails.. ?
It is useful to read: What does macroeconomics study?
Microeconomics, unlike macroeconomics, studies how and why specific people and companies make decisions, that is:
How does a particular firm use the money resources?
Why should consumers buy certain products?
How do one firm interact with another and with customers?
Useful to read: What problems does microeconomics consider?
Macroeconomics and Microeconomics: Common Features and Differences
Although there are few similarities between both – “economics”. Usually, in response to what is common, they say rather vaguely that “these two sciences are interconnected and influence each other.”
The cardinal differences between macro and microeconomics are as follows:
Object of study:
Micro-private (individuals, households, businesses)
Macro-global (world market)
Relationship to prices:
Micro – prices for individual goods
Macro – general price level
Working with data and statistics:
Macro – a lot of attention, a lot of assumptions
Micro – less assumptions, more facts
Markets studied:
Micro – a specific market
Macro – all markets in aggregate
Bottom line:
“Micro” – for business
“Macro” – for the country
Macroeconomics and microeconomics: examples
Three examples that clearly show how microeconomics differs from macroeconomics
Example 1
Microeconomics studies the question – how the price of real estate in Moscow and the regions of Russia changes.
And macroeconomics will be interested in global trends in real estate prices (for example, the impact of apartment prices in the United States on the general price market in Europe)
Example 2
Micro – what a startup needs to do to get investments in Silicon Valley.
Macro – general patterns of investment activity in the world
Example 3
Micro – studies why China is selling fewer smartphones.
Macro – how it will affect the global economy